
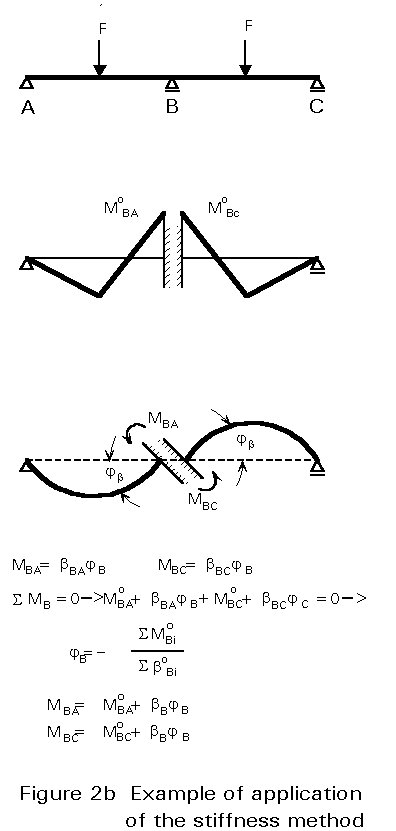
It provides readers with an understanding of the underlying methodologies of finite element analysis and the practices used by professional structural engineers. The available equilibrium equations are the two force equilibrium.


10.1a has two unknown displacements (u2, v2). Integrating classical and modern methodologies, this book explains complicated analysis using simplified methods and numerous examples. For example, the plane truss shown in Fig. of internal stresses in frames using force and displacement methods EXAMPLE. Other topics covered include influence lines, non-prismatic members, composite structures, secondary stress analysis, and limits of linear and static structural analysis. 1.0 Introduction to methods of structural analysis It is a well known fact. Toward the end of the book, the displacement method reappears along with the moment distribution and slope-deflection methods in the context of beam and rigid frame analysis. It also extends the force method to beam and rigid frame analysis. The book then presents the force method of analysis for plane trusses to illustrate force equilibrium, deflection, statistical indeterminacy, and other concepts that help readers to better understand the behavior of a structure. Also, as Figure 100 shows, it was possible to use the same process but only apply the displacement in one of the supports of the structure. This means that for each iteration, a displacement of 5mm is applied to the structure in both supports. To minimize any conceptual difficulty readers may have, the displacement method is introduced with the plane truss analysis and the concept of nodal displacement. For example, in this particular case, a total of 24 stages are calculated, displacing a total of 12cm. A matrix operations tutorial is also included for review and self-learning. It also shows how these methods are applied, particularly to trusses, beams, and rigid frames.Īcknowledging the fact that virtually all computer structural analysis programs are based on the matrix displacement method of analysis, the text begins with the displacement method. It also shows how these methods are applied, particularly to trusses, beīridging the gap between what is traditionally taught in textbooks and what is actually practiced in engineering firms, Introduction to Structural Analysis: Displacement and Force Methods clearly explains the two fundamental methods of structural analysis: the displacement method and the force method. A typical computer program should calculate the x-displacement u of all basic. Bridging the gap between what is traditionally taught in textbooks and what is actually practiced in engineering firms, Introduction to Structural Analysis: Displacement and Force Methods clearly explains the two fundamental methods of structural analysis: the displacement method and the force method. Matrix Structural Analysis the Stiffness Method.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
